
While doing this, the response of the pupil of both eyes is observed. While you are looking at a distant object, the examiner will briefly direct the beam of a small flashlight at one of your eyes a few times. Typically, pupil testing is performed in a dimly lit room. RELATED READING: Eye accommodation Pupil Testingĭuring a routine eye exam, your eye doctor or an assistant will inspect your pupils and perform testing of pupil function. This is called the accommodative pupillary response.

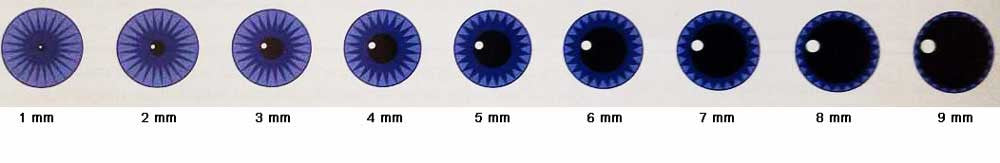
In addition to being affected by light, both pupils normally constrict when you focus on a near object. Generally, normal pupil size in adults ranges from 2 to 4 millimeters (mm) in diameter in bright light to 4 to 8 mm in the dark. Also, pupil size changes with age - children and young adults tend to have large pupils, and seniors usually have small pupils. The size of the pupil varies from person to person. In bright conditions, the pupil constricts to limit how much light enters the eye (too much light can cause glare and discomfort, and it may even damage the lens and retina). In low-light conditions, the pupil dilates so more light can reach the retina to improve night vision. This dynamic process of muscle action within the iris controls how much light enters the eye through the pupil. The size of the pupil is controlled by muscles within the iris - one muscle constricts the pupil opening (makes it smaller), and another iris muscle dilates the pupil (makes it larger). Using the analogy of a camera, the pupil is the aperture of the eye and the iris is the diaphragm that controls the size of the aperture. Together, the iris and pupil control how much light enters the eye. This is due to the intense light from the flash being reflected by the red color of the retina. Depending on your direction of gaze when the photo is taken, your pupils might appear bright red. Someone takes your photo using the camera's flash function. There's another common situation when the pupil of the eye changes color - when When the cloudy lens is replaced by a clear intraocular lens (IOL) during cataract surgery, the normal black appearance of the pupil is restored. If the pupil has a cloudy or pale color, typically this is because the lens of the eye (which is located directly behind the pupil) has become opaque due to the formation of a cataract. The black color is because light that passes through the pupil is absorbed by the retina and is not reflected back (in normal lighting). Typically, the pupils appear perfectly round, equal in size and black in color. The function of the pupil is to allow light to enter the eye so it can be focused on the retina to begin the process of sight. The pupil is the opening in the center of the iris (the structure that gives our eyes their color). For additional information visit Linking to and Using Content from MedlinePlus.One of the most important parts of the eye isn't a structure at all - it's an open space. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited without authorization. Links to other sites are provided for information only - they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy editorial process and privacy policy. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. Injury to the carotid or vertebral arteryĪ.D.A.M., Inc.Tumor, mass, or lymph node in the upper chest or lymph node causing pressure on a nerve may cause decreased sweating, a small pupil, or drooping eyelid all on the affected side (Horner syndrome).
Seizure (pupil size difference may remain long after seizure is over).



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
